Low-altitude economy | Drone logistics compliance guide: Core approval points that enterprises must master
Published:
2025-03-11
In March 2024, "low-altitude economy" was first included in the government work report, marking 2024 as the inaugural year for the development of the "low-altitude economy." By 2025, more than 30 provinces (municipalities directly under the central government) in the country will have included the development plan for the "low-altitude economy" in the 2025 government work report. With the convening of the Two Sessions, under the major theme of "new quality productivity," the low-altitude economy has also become a dark horse topic this year. As a strategic emerging industry, the development of the low-altitude economy is rapidly advancing under policy guidance.
In March 2024, "low-altitude economy" was first included in the government work report, marking 2024 as the inaugural year for the development of the "low-altitude economy". As we enter 2025, more than 30 provinces (municipalities) in the country have included the development plan for the "low-altitude economy" in the 2025 government work report. With the convening of the Two Sessions, the low-altitude economy has also become a dark horse topic this year under the major theme of "new quality productivity". As a strategic emerging industry, the development of the low-altitude economy is rapidly advancing under policy guidance.
Currently, the Applications of the low-altitude economy mainly include agricultural plant protection, logistics distribution, power inspection, cultural tourism entertainment, emergency rescue, etc. Among these, logistics distribution is the most widely used scenario for the commercialization of the low-altitude economy. In June 2024, SF Express launched a drone cargo line from Harbin to Mohe; in February 2025, the first large-scale intercity low-altitude logistics route in the country—from Yulin, Shaanxi to Xi'an—successfully made its maiden flight, officially starting large-scale drone trunk logistics transportation in the country. According to the "2024 China Low-altitude Logistics Development Report", the future market size of low-altitude logistics is expected to reach 120 billion to 150 billion yuan by 2025, and is likely to reach 450 billion to 605 billion yuan by 2035.
With the rapid development of the market, more and more enterprises are entering the drone logistics industry. How drone logistics companies can legally and compliantly conduct business has become one of the key factors to ensure the healthy development of the industry and enterprises. This article will provide a compliance operation guide for drone logistics companies to "take off" from the practical operation level.
I. Legal System and Approval Process Related to Drone Logistics Compliance
The legal system related to drone logistics compliance mainly consists of two modules. The first is the laws and regulations related to drone flight, mainly including the "Interim Regulations on the Flight Management of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles" and the "Safety Management Rules for Civil Unmanned Aerial Vehicles". The second consists of postal and express-related legal systems, including the "Postal Law of the People's Republic of China", the "Implementation Rules of the Postal Law of the People's Republic of China", and the "Management Measures for Express Business Operation Licenses". This article mainly discusses the laws and regulations related to drone flight, focusing on the key approval points related to the "take-off" of drone logistics companies during their operations.
According to the "Interim Regulations on the Flight Management of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles" and the "Safety Management Rules for Civil Unmanned Aerial Vehicles", before a drone "takes off", it is necessary to go through four major key approval processes: real-name registration, airworthiness certificate application, operation qualification certificate handling, and flight activity application and Confirm. The specific process is as follows:
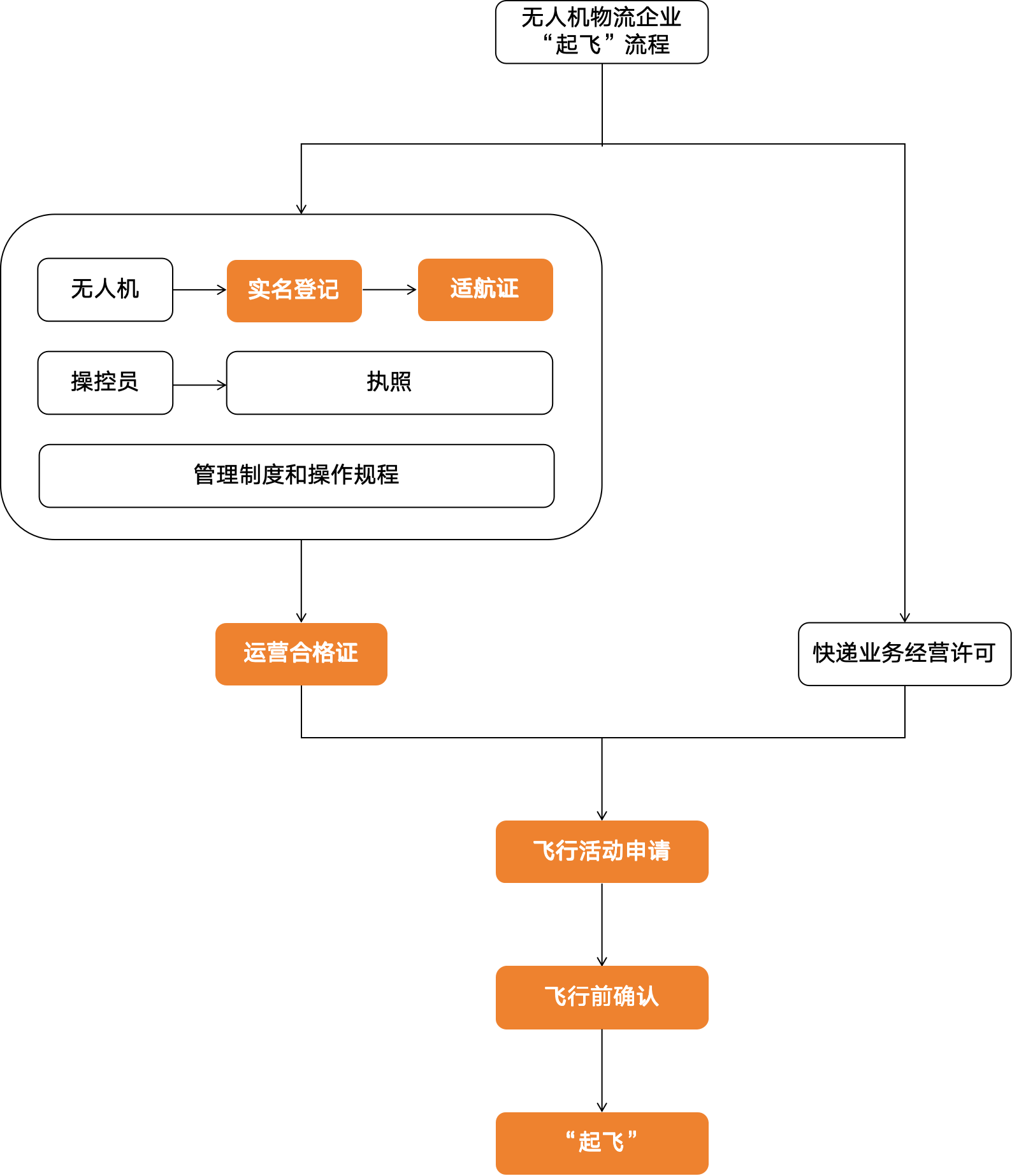
II. Real-name Registration of Civil Unmanned Aerial Vehicles
The first step in flying an unmanned aerial vehicle is to conduct real-name registration for the unmanned aerial vehicle.
1. Specific Operation Process for Real-name Registration
Article 10 of the "Interim Regulations on the Flight Management of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles" (hereinafter referred to as the "Interim Flight Management Regulations") stipulates that the owner of a civil unmanned aerial vehicle shall conduct real-name registration in accordance with the law; Article 92.201 of the "Safety Management Rules for Civil Unmanned Aerial Vehicles" (hereinafter referred to as the "Safety Management Rules") also stipulates that civil unmanned aerial vehicles engaged in flight and related activities within the territory of the People's Republic of China shall conduct real-name registration in accordance with the provisions of this chapter. The relevant requirements for real-name registration are detailed in Articles 92.205-92.214 of the "Safety Management Rules", which specifically include:
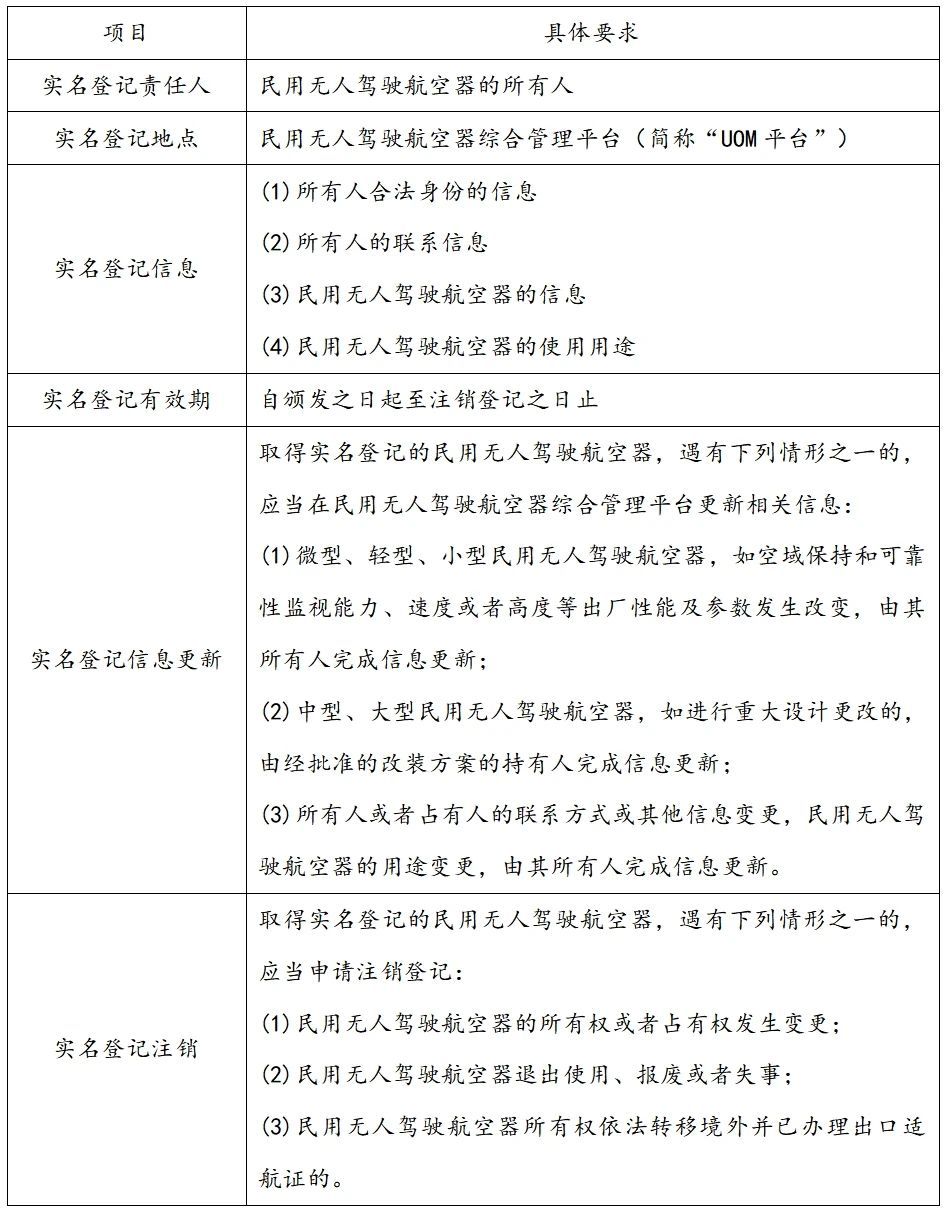
The first step for drone logistics companies to engage in related business is to conduct real-name registration for the purchased drones according to the above regulations. After registration, they can obtain a real-name registration mark from the UOM platform, including UAS and real-name registration number. The real-name registration mark for medium and large civil unmanned aerial vehicles should be affixed or sprayed on the civil unmanned aerial vehicle, kept clear and distinguishable, and easy to view. It is worth noting that drones that have completed real-name registration should also update their real-name registration information and cancel real-name registration on the UOM platform in a timely manner according to the above regulations.UOMIn addition, civil unmanned aerial vehicles engaged in overseas flights should also complete nationality registration and obtain nationality marks and registration marks.
2. Legal Risks of Conducting Flight Activities Without Real-name Registration
According to Article 47 of the "Interim Flight Management Regulations", if a civil unmanned aerial vehicle conducts flight activities without real-name registration, the public security organ shall order correction and may impose a fine of less than 200 yuan; if the circumstances are serious, a fine of more than 2,000 yuan and less than 20,000 yuan may be imposed. For civil unmanned aerial vehicles engaged in overseas flights that have not completed nationality registration in accordance with the law, the civil aviation management department shall order correction and impose a fine of more than 10,000 yuan and less than 100,000 yuan.
Therefore, drone logistics companies should conduct standardized real-name registration for drones in accordance with the requirements of the "Interim Flight Management Regulations" and the "Safety Management Rules" to avoid related legal risks that may affect the conduct of related businesses.
III. Application for Airworthiness Certificate for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles
The airworthiness certificate includes standard airworthiness certificates, special airworthiness certificates, special flight permits, and export airworthiness certificates. In the field of drone logistics, it mainly involves the application for standard airworthiness certificates and special airworthiness certificates. The standard airworthiness certificate is mainly applicable to normal and transport civil unmanned aerial vehicle systems that have obtained model qualification certificates. The special airworthiness certificate is applicable to limited-use civil unmanned aerial vehicle systems that have obtained model qualification certificates and those that should be conducted according to regulations.
Safety Assessmentof civil unmanned aerial vehicle systems.For new civil unmanned aerial vehicle systems manufactured after January 1, 2024, according to the production license, airworthiness inspection is not required. The owners or possessors of civil unmanned aerial vehicle systems that have completed real-name registration only need to submit an application and relevant documents proving the airworthiness of the aircraft system to the Civil Aviation Administration to obtain the airworthiness certificate.
For medium and large civil unmanned aerial vehicle systems that were designed and finalized before January 1, 2024, if they apply for an operation qualification certificate for civil aviation activities according to relevant regulations and do not make design changes, they can undergo safety assessment accepted by the Civil Aviation Administration before November 26, 2026, and obtain a special airworthiness certificate under the usage restrictions specified by the Civil Aviation Administration. Civil unmanned aerial vehicles that have obtained special airworthiness certificates may not be used for manned flights, may not conduct integrated flights, may not fly over densely populated areas on the ground, may not engage in overseas flights, and may only fly under the restrictions specified by the Civil Aviation Administration.
IV. Application for Operation Qualification Certificate for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles
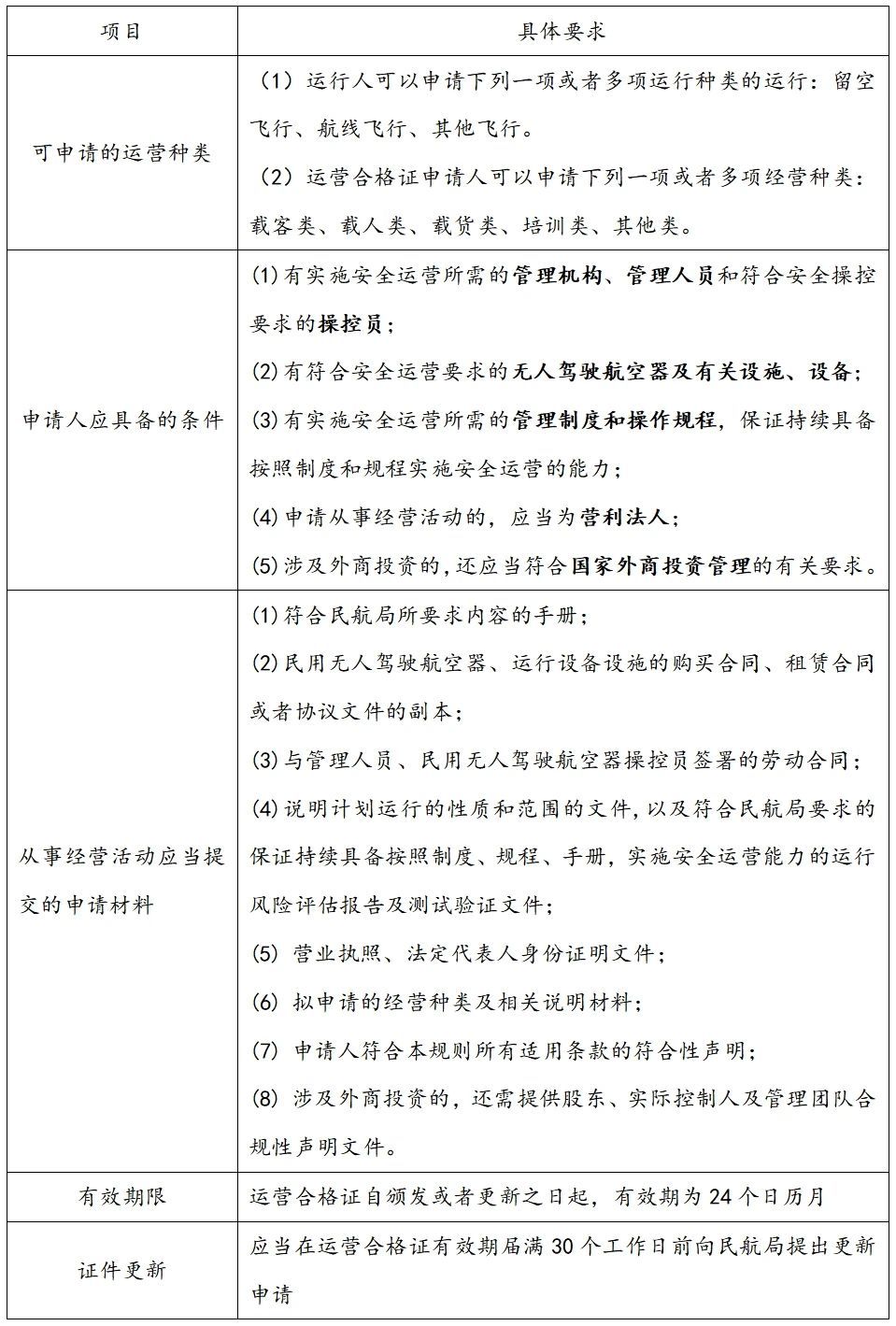
According to the "Interim Flight Management Regulations" and the "Safety Management Rules", except for using micro civil unmanned aerial vehicles for flight activities and conventional agricultural unmanned aerial vehicle operation activities, units using civil unmanned aerial vehicles for flight activities must undergo operational safety assessments by the Civil Aviation Administration or local civil aviation management bureaus (hereinafter collectively referred to as the "Civil Aviation Administration"), obtain the operation qualification certificate issued by the Civil Aviation Administration, and comply with the corresponding operational specifications before they can implement operations.
According to the "Safety Management Regulations", the conditions and procedures for obtaining the operation qualification certificate are as follows:
According to Article 49 of the "Interim Flight Management Regulations" and Article 92.1005 of the "Safety Management Rules", if flight activities are conducted without obtaining an operation qualification certificate or in violation of the requirements of the operation qualification certificate, the civil aviation management department shall order correction and impose a fine of more than 50,000 yuan and less than 500,000 yuan; if the circumstances are serious, they shall be ordered to suspend business for rectification until their operation qualification certificate is revoked.
根据《飞行管理暂行条例》第四十九条及《安全管理规则》92.1005条,未取得运营合格证或者违反运营合格证的要求实施飞行活动的,由民用航空管理部门责令改正,处5万元以上50万元以下的罚款;情节严重的,责令停业整顿直至吊销其运营合格证。
Therefore, before operating, drone logistics companies should obtain an operating license according to the above regulations.
5. Airspace and Flight Activity Application
1. Airspace Suitable for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles
The Interim Regulations on Flight Management stipulate that airspace above a true altitude of 120 meters, restricted airspace, controlled airspace, surrounding airspace, military aviation ultra-low altitude flight airspace, as well as airspace above important infrastructure such as airports, national borders, military restricted areas, power plants, and radio astronomy observatories that require special electromagnetic environment protection, and important revolutionary memorial sites should be designated as controlled airspace. Unmanned aerial vehicle flight activities shall not be conducted in controlled airspace without the approval of air traffic management authorities. Airspace outside the controlled airspace is suitable for micro, light, and small unmanned aerial vehicles.
That is to say, outside the controlled airspace, micro, light, and small unmanned aerial vehicles can fly freely without applying for flight activities. The suitable airspace for unmanned aerial vehicles within China can be queried through the UOM platform.
In the field of drone logistics, short-distance and small cargo transportation can use micro or light drones, but intercity logistics and general cargo transportation require medium to large drones, which necessitates applying for flight activities in advance.
2. Flight Activity Application
Flight activities of unmanned aerial vehicles within China can be applied for through the UOM platform. Organizations or individuals organizing unmanned aerial vehicle flight activities should submit a flight activity application through the UOM platform at least 12 hours before the planned flight.
If the airspace involved in drone logistics is relatively fixed, a regular flight activity application can also be made. Regular flight refers to unmanned aerial vehicles performing the same task in the same airspace, with a certain time span and flight frequency. For regular flight activities conducted in fixed airspace, applications can be submitted 3 days before the first flight activity, and air traffic management authorities will make a decision to approve or disapprove the application 1 day before the flight activity.
In addition, approved flight activities must be confirmed before takeoff. Organizations or individuals that have obtained approval for flight activities should report the expected takeoff time and preparation status to air traffic management authorities 1 hour before the planned takeoff. Takeoff can only occur after confirmation from the air traffic management authorities.
6. Summary
On December 27, 2024, the Low Altitude Economic Development Department of the National Development and Reform Commission was officially established, which means that the country is placing greater strategic importance on the low altitude economy, viewing it as a new economic growth point. Based on this, many companies are eager to try and prepare to seize the opportunity.
However, the characteristics of the low altitude economic industry chain being long, involving many industries and links, and having high safety requirements also mean that the low altitude economy will inevitably be a highly regulated field, which raises higher compliance requirements for companies. At the same time, corresponding to the industry's start, the legal and regulatory system in the low altitude economic field will also be updated rapidly. Companies should view the legal risks in the operational process with a dynamic mindset, ensuring that they operate within the legal and compliant "channel". This is not only a protection for themselves but also a contribution to the healthy and stable development of the industry.
Key words:
Previous article
Related News

Zhongcheng Qingtai Jinan Region
Address: Floor 55-57, Jinan China Resources Center, 11111 Jingshi Road, Lixia District, Jinan City, Shandong Province



