20
2021-12
Viewpoint | Analysis of the reliability of patent protection
It is generally believed that the value of patent rights includes legal value, technical value and economic value. The reliability of patent protection is an important index to evaluate and analyze the legal value of patent. The so-called reliability of patent protection refers to the reliability of the patentee or patent user in the face of the suspected infringing object, using the current infringement determination rules to determine whether the suspected infringing object falls into the scope of specific patent protection. Through the analysis of the stability of the specific patent itself and the restriction degree of the following patent, the probability of a specific patent winning a patent infringement lawsuit is judged. This paper will start with the writing quality of the claims and instructions to analyze the reliability of patent protection, so it is only applicable to inventions or utility models, not design. The author thinks that the reliability of patent protection can be analyzed comprehensively from the five dimensions of patent category, patent text quality, restriction degree of implementation, restriction degree of following patent and stability, so as to draw a more objective expectation judgment on whether infringement is established in patent infringement litigation. 1. patent category According to China's current patent examination and authorization rules, utility model patents can be authorized only through formal examination, while invention patents can only be authorized after passing formal examination and passing substantive examination. Therefore, the stability of a particular patent can be judged by the type of patent and the nature of the invention, and it is clear that the stability of the invention patent is higher than that of the utility model patent. In addition, starting with the layout of the claims, the independent claim is a product claim and has more subordinate claims, which is better than only one product claim, and then better than only the method claim. 2. patent text quality The consideration of the quality of the patent text should include at least the following three aspects: first, the writing quality of the independent claims; second, the layout and writing quality of the dependent claims; third, the clarity and completeness of the patent specification and the support for the claims. An ideal authorized patent should meet all the following conditions:(1) the patent specification provides a clear and complete description of the invention and creation, and the embodiments are specific, to the extent that can be realized by those skilled in the art in combination with the accompanying drawings;(2) The independent claims are supported by the specification, with clear expressions and appropriate generalizations;(3) The subordinate claims are reasonably arranged and have a considerable number of subordinate claims;(4) There is no case where the amendment provided for in Article 33 of the Patent Law exceeds the scope. Obviously, if a patent deviates more and more negatively from the above conditions, the text quality will be worse. Constraints on 3. implementation The purpose of this indicator is to analyze whether a specific patented technical solution falls within the scope of protection of the prior patent, and if so, the implementation of the specific patent requires the permission of the prior patentee, otherwise the prior patent will be infringed. In the specific judgment method, after searching, compare a particular patent with a closest prior patent, determine the degree of overlap with the prior patent independent claim, and determine whether the two constitute equivalent if there is a difference in technical characteristics. Obviously, if there is a substantial difference between a particular patent and the nearest prior patent, and the technical characteristics of the independent claim are significantly different, then the particular patent can be implemented independently and is not subject to the surviving patent, which is the best. If a particular patent is subject to a prior patent, but the prior patent clearly has a flaw that has been declared invalid or if the particular patent has room to avoid the prior patent, it is an intermediate result. If a particular patent falls within the scope of prior patent protection and lacks substantive characteristics relative to the prior patent, it is a poor result. 4. degree of restriction on following patents This indicator is used to determine the degree of restriction of a particular patent on the implementation of a subsequent follow-up improvement technology, I .e., the probability of a subsequent follow-up technology avoiding a particular patent infringement. In the specific method, compare the specific patent with the following patent, and analyze whether the specific patent can effectively restrict the independent implementation of the following patent relative to the specific patent. Obviously, it is best if the follow-up patent is not retrieved, or if the follow-up patent falls unquestionably within the scope of protection of a particular patent. If, although there are different technical characteristics between the following patent and the specific patent, there is no substantial difference, that is, the following patent has a high probability of falling into the scope of protection of the specific patent, is also a better result. If the follow-up patent does not fall within the scope of protection of the particular patent, I .e. the follow-up patent can be implemented freely without the restriction of the particular patent, then the value of the particular patent will be diminished. 5. stability This indicator is used to determine the possibility of invalidation of a particular patent. Compare the specific patent with the existing technology before the filing date, and determine whether the specific patent has the risk of being declared invalid as stipulated in Article 65 of the Regulations of the Patent Law. Under this index system, the stability of patents with more distinguishing technical features is higher than that of patents with less distinguishing technical features. If a particular patent independent claim has more distinguishing technical features that are materially different from the combination of more than one prior art, then the probability of that particular patent being declared invalid is small and optimal. If a particular patent independent claim has few or no distinguishing technical features that differ materially from a combination of prior art within 3 articles, then the probability that the particular patent will be invalidated is high and is a poor result. If a particular patent independent claim has several distinguishing technical features compared with the combination of 3 or so existing technologies, but it is doubtful whether the distinguishing technical feature is a replacement of customary technical means, then the probability of the particular patent being declared invalid is in the middle. To sum up, according to the relevant provisions of China's Patent Law, Detailed Rules for the Implementation of the Patent Law and Patent Examination Guidelines, the author takes the quality of patent text as the main line, combines the characteristics of invention or utility model patents, and discusses the reliability of patent protection from five aspects: patent category, patent text quality, restriction degree of patent implementation, restriction degree of patent to follow patent, and stability of patent, the legal restriction effect of specific patented technology on the related technology in the same technical field is given objectively, and the result probability of infringement litigation is expected.
2021-12-20
20
2021-12
The revocation of the arbitral award needs to meet the statutory requirements, and this paper focuses on the analysis of whether the arbitral tribunal's failure to make an arbitral award within the statutory time limit constitutes a violation of the statutory procedure in the arbitral procedure and leads to the revocation of the arbitral award. 1. [link to the law]] the People's Republic of China Arbitration Act Article 58 If the parties provide evidence to prove that the award has one of the following circumstances, they may apply to the intermediate people's court where the arbitration commission is located to cancel the award. (I) there is no arbitration agreement; The matters awarded by the (II) do not fall within the scope of the arbitration agreement or the arbitration commission does not have the power to arbitrate; (III) the composition of the arbitration tribunal or the arbitration procedure violates the legal procedure; (IV) the evidence on which the award is based is falsified; (V) the opposing party conceals evidence sufficient to affect a just decision; (VI) arbitrators have solicited or accepted bribes, practiced favoritism, or perverted the law in adjudicating the case. If the people's court, after forming a collegial panel to examine and verify the award, has one of the circumstances specified in the preceding paragraph, it shall rule to cancel the award. If the people's court determines that the award is contrary to the public interest, it shall rule to cancel it. Interpretation of the Supreme People's Court on Several Issues Concerning the Application of the the People's Republic of China Arbitration Law Article 20 The term "violation of legal procedures" as stipulated in Article 58 of the Arbitration Law refers to the circumstances in which the violation of the arbitration procedures stipulated in the Arbitration Law and the arbitration rules chosen by the parties may affect the correct award of the case. 2. Typical Case] Case 1: The case of Company A and Company B applying for setting aside the arbitral award. On November 11, 2019, Chen and Company B filed an application for arbitration in this case to the Beijing Arbitration Commission. The respondent was Company A. After the Beijing Arbitration Commission formally accepted the case on November 18, 2019, it was held on December 31, 2019. Form an arbitration tribunal. In accordance with the arbitral award made on 8 March 2021, the arbitral tribunal of summary proceedings shall, in accordance with the provisions of the Arbitration Rules, make an award within 75 days from the date of the formation of the tribunal. If there are special circumstances that require an extension, the sole arbitrator shall submit it to the Secretary-General for approval, and the extension may be appropriately extended. Company A believes that the arbitration award made by the Arbitration Commission on March 8, 2021 exceeds the above-mentioned time limit, and requests the court to revoke the (2021) Beijing Arbitration Zi No. XXX award made by the Arbitration Commission in accordance with the law. The court held that this case was a case in which the parties applied for the revocation of the domestic arbitration award and should be reviewed in accordance with Article 58 of the the People's Republic of China Arbitration Law. Article 58 of the the People's Republic of China Arbitration Law stipulates that if the parties provide evidence to prove that the award has one of the following circumstances, they may apply to the intermediate people's court where the arbitration commission is located for cancellation of the award: (1) there is no arbitration agreement; the matters on which the award is (II) do not fall within the scope of the arbitration agreement or the arbitration commission has no power to arbitrate; the composition of the arbitration tribunal or the arbitration procedure violates legal procedure; the evidence on which the (IV) award is based is forged; the other party to the (V) has concealed evidence sufficient to affect the fairness of the award; the (VI) arbitrator has solicited and accepted bribes, practiced favoritism, or perverted the law in the arbitration of the case. If the people's court, after forming a collegial panel to examine and verify the award, has one of the circumstances specified in the preceding paragraph, it shall rule to cancel the award. If the people's court determines that the award is contrary to the public interest, it shall rule to cancel it. The above-mentioned provisions are the statutory reasons for the people's court to revoke the domestic arbitral award. With regard to Company A's claim that the arbitration procedure violates the legal procedure, the Court holds that the "violation of legal procedure" stipulated in Article 58 of the the People's Republic of China Arbitration Law refers to the situation that the violation of the arbitration procedure stipulated in the Arbitration Law and the arbitration rules chosen by the parties may affect the correct award of the case, and the violation of legal procedure shall seriously affect the procedural rights of the parties and substantially affect the correct award of the case. With regard to the fact that the award involved in the case was heard by a sole arbitrator, the Beijing Arbitration Commission made a clear statement on the matter. In addition, in accordance with Article 54, paragraph (I), and Article 55, paragraph (I), of the Arbitration Rules, the arbitration involved in the case was filed on the basis of the parties' arbitration request, which met the conditions for the application of the summary procedure in the Arbitration Rules, and it was not improper for the sole arbitrator to hear the case. Article 58 of the Arbitration Rules stipulates that if the amount of the dispute in the case exceeds 5 million yuan due to the change of the arbitration request, the summary procedure shall not be affected. Regarding the extension of the trial limit of the arbitration involved in the case, the case was applied by the sole arbitrator and approved by the Secretary-General of the Beijing Arbitration Commission to extend the trial limit, which does not violate the provisions of the Arbitration Rules. In addition, the arbitration tribunal heard all the arbitration requests of Chen Mou and Company B and the defense of Company A, investigated the relevant facts of the case, and organized both parties to provide evidence and cross-examine the evidence. The two parties debated around the focus of the dispute. Before the end of the trial, the two parties issued their final statements. No company A's rights were infringed. Therefore, the court did not support company A's claim. Case 2: The case of Xu and Chen's application to set aside the special procedure of the arbitral award. On September 23, 2009, Xu filed an arbitration application with the Yangzhou Arbitration Commission in accordance with the arbitration clause agreed in the contract, requesting the cancellation of the equity transfer agreement signed on October 16, 2008. The Yangzhou Arbitration Commission accepted Xu's arbitration request on September 24, 2009, and served relevant materials to the respondent Chen. On 26 November 2009, the Tribunal held its first hearing. On 19 and 20 December 2009, the Tribunal held its second session. On January 30, 2010, Xu filed an application for withdrawal from the chief arbitrator Xing. On February 8, 2010, Yangzhou Arbitration Commission made (2009) decision No. 668-1, deciding to reject Xu's application for chief arbitrator Xing to withdraw. On August 23, 2010, Yangzhou Arbitration Commission delivered the decision to Xu and Chen. … On July 5, 2016, Yangzhou Arbitration Commission made Award (2009) Yang Arbitration Zi No. XX, which was served on Xu and Chen on July 27, 2016. Xu later considered that the arbitral award had exceeded the statutory time limit and requested that it be set aside. Court view: on the question of whether the arbitration proceedings are illegal. Article 46 of the Yangzhou Arbitration Rules stipulates: "The arbitral tribunal shall make an arbitral award within four months after the formation of the arbitral tribunal. If there are special circumstances that require an extension, the chief arbitrator or the sole arbitrator may report to the chairman of the arbitration commission for approval, and the extension may be appropriately extended." According to this provision, four months is the time limit that the arbitral tribunal should abide by. Even if it needs to be extended, it should be appropriately extended, and the extended time limit should be specified when handling the application and approval procedures. The arbitral award involved in the case took 6 years and 8 months from the formation of the arbitral tribunal on November 2, 2009 to the service of the arbitral award to the parties on July 27, 2016, far exceeding the four-month period stipulated in the Yangzhou Arbitration Rules. Although the arbitral tribunal applied for an extension of the trial period on the grounds of the complexity of the case, no specific time limit was determined at the time of application and approval, resulting in an extension of the arbitration period for more than six years, a serious departure from the provisions of the Yangzhou Arbitration Rules on the period of award. The arbitration case file also reflects that the arbitration tribunal's trial activities were mainly concentrated before the end of 2010, and the trial activities were basically stagnant from 2011 to 2012, and no trial activities were carried out for more than three years from 2013 to 2015. The applicant Xu has written to the arbitration tribunal many times to request the award as soon as possible, but it was not until July 2016 that the arbitration tribunal made a final award. It is therefore clearly inappropriate for the arbitral tribunal to extend a period sufficient to give the parties reasonable doubt as to the fairness of the arbitral proceedings. The Court needs to emphasize that "to ensure fair and timely arbitration of economic disputes and to protect the legitimate rights and interests of the parties" is the basic legislative purpose of China's arbitration law. As we all know, the procedure design of arbitration system is to achieve the value goal of fair and timely settlement of disputes. This is an important reason why the parties choose arbitration to resolve disputes, and it is also an important basis for the survival and development of the arbitration system. However, the arbitration tribunal in this case did not adjudicate for a long time without legitimate reasons and justifiable reasons, and the arbitration period lasted as long as six years and eight months, resulting in a long-term unstable legal relationship between the parties and unable to obtain timely and effective relief, which seriously damaged the legitimate rights and interests of the parties, the arbitral award involved in the case seriously violates the provisions of Article 51, paragraph 1, of the the People's Republic of China Arbitration Law and Article 42, paragraph 1, and Article 46 of the Yangzhou Arbitration Rules, which may affect the correct award of the case and should be revoked in accordance with the law. Summary of 3. Lawyers From the above cases 1 and 2, it can be seen that failure to make an arbitration award within the prescribed time limit does not constitute a violation of the arbitration procedure stipulated in the third paragraph of Article 58 of the Arbitration Law and a violation of the legal procedure. The "circumstances that may affect the correct award of the case" stipulated in Article 20 of the Interpretation of the Supreme People's Court on Several Issues Concerning the Application of the the People's Republic of China Arbitration Law shall also apply." After comprehensive consideration, if it is necessary to extend the arbitration trial period due to special circumstances such as complex circumstances or epidemic situation, it will not affect the correct award of the case, and the arbitration award cannot be revoked according to this clause. On the contrary, arbitration is an efficient and convenient way to resolve disputes. If the arbitration tribunal does not issue an award for a long time without justifiable and legal reasons, and it will affect the rights of the parties and the correct award of the case, the court may set aside the arbitral award accordingly.
2021-12-20
18
2021-12
On December 16, 2021, Song Huidong, a senior partner of Zhongcheng Qingtai Jinan Institute and director of Urban Construction Real Estate Department, was invited by Jinan Urban Construction Group Co., Ltd. to carry out special special legal training on enterprise retirement. More than 40 responsible comrades of relevant departments and subsidiaries of the construction group participated in this training. Lawyer Song Huidong combined with years of practical experience in handling "zombie enterprises" for major state-owned enterprises and group companies in Shandong Province and Jinan City, conducted in-depth analysis through practical cases, and at the same time combined with relevant legal provisions on company liquidation and cancellation, explained the conditions for company liquidation and cancellation, the key work items of the Construction Group in the liquidation and cancellation procedures, the company's own liquidation and company bankruptcy liquidation procedures, etc. It provides comprehensive and professional legal support for the construction group in the liquidation and cancellation of enterprises, such as assets and capital verification, financial audit, creditor's rights recovery, personnel placement, etc. It has improved the legal professional quality and ability of enterprise managers, ensured that enterprise disposal procedures are in compliance with the law, and ensured the safety and integrity of state-owned assets. The participants spoke highly of the training, believing that the training content was comprehensive and professional, which deepened the group employees' understanding of enterprise liquidation, enhanced the employees' awareness of risk prevention in the process of enterprise creditor's rights recovery and asset disposal, provided effective response measures for disposal enterprises, and laid a good foundation for the group's actual work in enterprise liquidation and cancellation in the future.
2021-12-18
17
2021-12
一、问题提出 《中华人民共和国公司法》(以下简称《公司法》)第十六条规定了公司对外担保制度,规定如下: “公司向其他企业投资或者为他人提供担保,依照公司章程的规定,由董事会或者股东会、股东大会决议;公司章程对投资或者担保的总额及单项投资或者担保的数额有限额规定的,不得超过规定的限额。 公司为公司股东或者实际控制人提供担保的,必须经股东会或者股东大会决议。 前款规定的股东或者受前款规定的实际控制人支配的股东,不得参加前款规定事项的表决。该项表决由出席会议的其他股东所持表决权的过半数通过。” 《公司法》第十六条的第二、第三款是关于公司为股东或者实际控制人提供担保的规定,《公司法》对这种担保进行了程序上的限制,即由“其他股东”对担保进行表决,由此便产生一个问题,如果没有“其他股东”对外担保应如何表决。一人有限责任公司包括自然人独资的有限责任公司和法人独资的全资子公司两种情况,因一人公司不设股东会,如果依据《公司法》第十六条第二、第三款规定的股东会根本无法召开,此时公司能否为股东提供担保就成为了疑问。换句话说,一人有限责任公司为其股东提供担保的效力及后果如何? 在《民法典》和《最高人民法院关于适用<中华人民共和国民法典>Prior to the introduction of the Interpretation of the Guarantee System, there was considerable controversy in judicial practice regarding the effectiveness of a one-person company's guarantee for its shareholders. One point of view is that according to the provisions of paragraphs 2 and 3 of Article 16 of the Company Law, when a company provides guarantees for its shareholders, it must be resolved by the shareholders' meeting or the shareholders' meeting, and the guaranteed shareholders are not allowed to participate in the voting. The voting is approved by more than half of the voting rights held by other shareholders present at the meeting. In the case of a one-person company providing guarantees for shareholders, not only can it not form an effective shareholders' meeting resolution, it cannot even convene a shareholders' meeting, therefore, a contract entered into by a one-person company to provide security for shareholders should be considered invalid. Another view was that, according to article 63 of the Companies Act, the personality of a one-person company was presumed to be confused with the personality of its shareholders, and that, therefore, the provision of a guarantee by a one-person company for its shareholders should be understood as a guarantee by the company for itself, even if the company was unable to form a valid resolution in that regard, it would not affect the validity of the guarantee. 2. classic case 1. Viewpoint 1: The provisions of Article 16 of the Company Law are regulatory rather than effective norms. Case No.: Supreme People's Court (2012) Minti Zi No. 156 Case excerpt: The Court believes that the focus of the dispute between the parties in this case is the definition of the responsibility of the guarantor Zhenbang Co., Ltd. In view of the fact that the loan contract involved in the case has been determined to be valid for a court of second instance, and the applicant for retrial has no objection to this, the Court directly confirms the validity of the loan contract involved in the case. The Mortgage Contract and the Irrevocable Guarantee are guarantees made by the guarantor Zhenbang Co., Ltd. to the creditor Donggang Branch of China Merchants Bank for the liabilities of its shareholder Zhenbang Group Company. As a company organization and corporate behavior, it is regulated by the Company Law, and its external guarantee in the form of contract is also subject to the contract law and the security law. The determination of the validity of the company's guarantee contract in the case, because it does not go beyond the scope of the contractual act between equal commercial subjects, should first be judged from the relevant provisions of the contract law. With regard to the validity of a contract, Article 52 of the the People's Republic of China Contract Law (hereinafter referred to as the Contract Law) stipulates that "a contract shall be null and void under any of the following circumstances. ...... (V) violate the mandatory provisions of laws and administrative regulations". Regarding the "mandatory" in the aforementioned law, Article 14 of the Supreme People's Court's "Interpretation (II) on Several Issues Concerning the Application of the the People's Republic of China Contract Law" (hereinafter referred to as the Contract Law Interpretation II) makes the following interpretation and stipulates that "The" mandatory provisions "stipulated in Item (V) of Article 52 refer to effective mandatory provisions". Therefore, the law and relevant judicial interpretations have made it clear that violation of the mandatory norms of validity in laws or administrative regulations is one of the criteria for determining the validity of contracts. As a legal entity different from a natural person, the company's contractual behavior, while accepting the regulation of contract law, is subject to the company law as a special norm of the company. Article 1 of the Company Law clearly stipulates that "in order to regulate the organization and behavior of companies, protect the legitimate rights and interests of companies, shareholders and creditors, maintain social and economic order, and promote the development of the socialist market economy, this law is formulated". Article 16, paragraph 2, of the Company Law stipulates: "Where a company provides guarantees for the shareholders or actual controllers of the company, it must be resolved by the shareholders' meeting or the general meeting of shareholders". The above-mentioned provisions of the Company Law have made it clear that its legislative intent is to restrict the subject behavior of the company and prevent the actual controller or senior management of the company from harming the interests of the company, minority shareholders or other creditors, so its essence is an internal control procedure, which cannot be used to restrain the counterparty of the transaction. The above provisions should therefore be understood as regulatory peremptory norms. In principle, it is inappropriate to find the contract invalid in violation of this norm. In addition, if it is determined as a criterion of validity, it will reduce the efficiency of transactions and damage the security of transactions. For example, when the shareholders' meeting will be held, in what form, and who can express the true will on behalf of the shareholders are beyond the judgment and control ability of the counterparty of the transaction. If the contract is ruled invalid by violating the shareholder resolution procedure, it will definitely reduce the transaction efficiency. At the same time, it also leaves a system gap for the company to easily violate the shareholder resolution and claim that the contract is invalid, ultimately endangering the transaction safety, it is not only against the rules of good faith in commercial conduct, but also against fairness and justice. Therefore, 1. the court of second instance in this case, on the grounds that the resolution of the "guarantee resolution of the shareholders' meeting" involved in the case has not been approved by the shareholders' meeting of Zhenbang Co., Ltd., and Zhenbang Co., Ltd. has not held a shareholders' meeting on this matter, according to Article 16 of the Company Law, it is an error of applicable law to make a determination that the irrevocable guarantee and the mortgage contract are invalid, and the court will correct it. 2. Viewpoint 2: Article 16 of the Companies Act does not apply to one-person limited liability companies. Case No.: Sichuan Higher People's Court (2014) Chuan Min Di Zi No. 334 Excerpts from the case: the issue of the law applicable to the original judgment. 1. Whether the Ritz Hotel is liable for the guarantee. First of all, the "the People's Republic of China Company Law" and related judicial interpretations do not clearly stipulate whether a one-person limited liability company can provide guarantees for shareholders' debts, and based on the principle of freedom of contract, a one-person limited liability company can guarantee shareholders' debts. Secondly, Article 16 of the the People's Republic of China Company Law stipulates: "if a company invests in other enterprises or provides guarantee for others, it shall be decided by the board of directors or the shareholders' meeting or the general meeting of shareholders in accordance with the provisions of the articles of association; if the articles of association stipulate the total amount of investment or guarantee and the amount of individual investment or guarantee, it shall not exceed the prescribed limit. Where a company provides a guarantee for the shareholders or actual controllers of the company, it must be resolved by the shareholders' meeting or the general meeting of shareholders. The shareholders specified in the preceding paragraph or the shareholders controlled by the actual controller specified in the preceding paragraph shall not participate in the voting on the matters specified in the preceding paragraph. The vote was passed by a majority of the voting rights held by other shareholders present at the meeting." The legislative purpose of this article is to restrict related party transactions. The guarantee provided by the company for shareholders or actual controllers is a related party transaction, which may harm the interests of the company and other shareholders. Therefore, the second paragraph of Article 16 of the the People's Republic of China Company Law stipulates that the provision of related party guarantee for shareholders or actual controllers must be voted by the shareholders' meeting or the general meeting of shareholders, and cannot be decided by the board of directors through the articles of association. At the same time, the third paragraph of the article stipulates that shareholders or shareholders controlled by actual controllers shall abstain from voting. It can be seen that the law does not prohibit related guarantees, but through a special resolution mechanism in the internal governance of the company to achieve the risk control of related guarantees. For a one-person limited liability company, there is only a single shareholder, and there is no situation in which major shareholders use related party transactions to harm the interests of the company or minority shareholders. After long Zhaogang and Zhou Lin transferred their shares to Yang Guang in this case, the company is a one-person company and does not have the prerequisites for the application of paragraphs 2 and 3 of Article 16 of the the People's Republic of China Company Law. Furthermore, Article 61 of the the People's Republic of China Company Law stipulates: "A one-person limited liability company shall not have a shareholders' meeting. When the shareholders make the decisions listed in the first paragraph of Article 38 of this Law, they shall be in writing and shall be signed by the shareholders and kept in the company." Therefore, a one-person limited liability company does not have a shareholders' meeting, so it is naturally impossible to establish a shareholders' meeting and form a resolution of the shareholders' meeting. The ownership and management rights of the company are not separated and are exercised by the owner of the company, that is, the sole shareholder. Since the shareholders of a one-person limited liability company can exercise all the functions and powers of the shareholders' meeting, it should include making a decision that the company guarantees the debts of the shareholders. Therefore, Article 16 of the the People's Republic of China Company Law does not apply to one-person limited liability companies. 3. the views of our lawyers Due to the lack of community nature of one-person companies, there has been considerable controversy over whether the Company Law should recognize one-person companies in the process of amending the Company Law. The Company Law, as amended in 2005, adopts a compromise approach, I .e., while recognizing a one-person company, adopts an inversion of the burden of proof, providing that shareholders are jointly and severally liable for the debts of the company if they are unable to prove that the company's property is independent of their own property. In the case of a one-person company providing a guarantee for shareholders, whether the guarantee contract is found to be invalid because there is no resolution of the shareholders' meeting is a more controversial issue in practice. We believe that the company law makes it clear that its legislative intention is to restrict the main body of the company and prevent the actual controller or senior management of the company from harming the interests of the company, minority shareholders or other creditors. Therefore, its essence is an internal control procedure, which cannot restrict the counterparty of the transaction. Although a one-person company has an independent personality in form, in the case that the shareholders do not prove that the company's property is independent of the shareholder's property, the personality of the company will be presumed to be confused with the personality of the shareholders, so we can understand the guarantee provided by a one-person company to the shareholders as the company guarantees its own debts, and the company resolution is not a necessary condition. In other words, if a one-person company, after providing a guarantee for shareholders, requests the people's court to determine that the guarantee contract is invalid on the grounds that there is no resolution of the shareholders' meeting, the people's court shall not support it. In addition, the Supreme People's Court on the application of<中华人民共和国民法典>有关担保制度的解释》第10条对上述观点提供了法律依据,“一人有限责任公司为其股东提供担保,公司以违反公司法关于公司对外担保决议程序的规定为由主张不承担担保责任的,人民法院不予支持。公司因承担担保责任导致无法清偿其他债务,提供担保时的股东不能证明公司财产独立于自己的财产,其他债权人请求该股东承担连带责任的,人民法院应予支持。”综上,我所律师倾向于认为一人有限责任公司为股东提供担保具有法律效力,在没有公司决议的情况下公司以违反对外担保决议程序主张不承担担保责任的不应得到支持。</中华人民共和国民法典></中华人民共和国民法典>
2021-12-17
16
2021-12
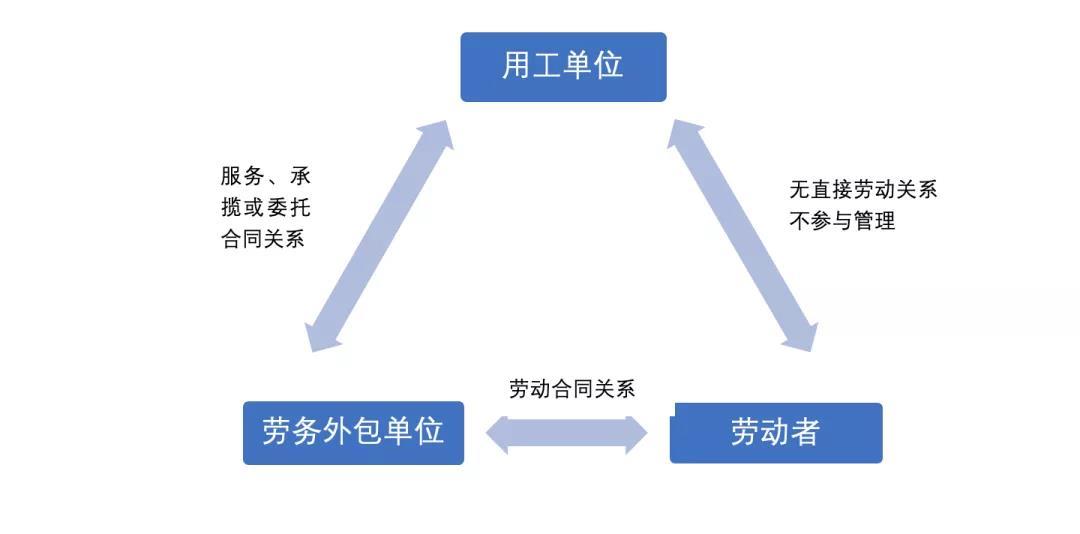
In practice, most of the proposed IPO enterprises have more or less labor problems, and with more and more enterprises adopting the labor outsourcing model, the CSRC is paying more and more attention to the labor outsourcing problem. This paper summarizes the difference between labor outsourcing and labor dispatch, and analyzes the focus of the audit of labor outsourcing and labor dispatch by the regulatory authorities in the IPO, with a view to learning and discussing with you. 1. what is labor outsourcing? Labor outsourcing refers to the business outsourcing mode in which an enterprise contracts part of its business or function to the relevant labor service organization, and the labor service organization arranges the labor service personnel to complete the corresponding business or work according to the specific needs of the enterprise. Under the labor outsourcing mode, there is no actual employment relationship between the enterprise and the worker, so there is no need to bear the obligations of the employer. To some extent, labor outsourcing can save the labor cost of the enterprise and reconfigure the various resources of the enterprise according to the business characteristics of the enterprise. Its basic legal relationship is shown in the following figure: In the June 2020 revision of the CSRC's "Questions and Answers to Certain Questions on Initial Business", question 47 answers the situation related to the outsourcing of labor services of the initial enterprise: "Question 47, the outsourcing of labor services of the initial enterprise, what aspects should the intermediary focus on? A: Some of the first-time enterprises have handed over more labor activities to specialized labor outsourcing companies for implementation. Intermediary agencies should pay full attention to the following aspects:(1) the legal compliance of the labor service companies, such as whether they are independent entities, whether they have the necessary professional qualifications, whether the business implementation and personnel management comply with relevant laws and regulations, the background of the business transactions between the issuer and the issuer and whether there are major risks;(2) whether the labor service company specializes or mainly serves the issuer, if there is a situation that mainly serves the issuer, attention should be paid to its reasonableness and necessity, and whether the identification and disclosure of related relationships are true, accurate and complete. Intermediary agencies shall check such situations according to the relevant requirements of related parties from the perspective of substance over form, and especially consider the impact of their operating results on the issuer's financial data and whether the issuer meets the issuance conditions;(3) The composition and changes of the labor service company, the main contents of the labor service outsourcing contract, whether the changes in the number of labor services and expenses match the issuer's operating performance, whether the pricing of labor costs is fair and whether there is an inter-period accounting situation. Intermediaries should make full arguments on the above aspects and express clear opinions." In recent years, when the CSRC approves the listing of enterprises, many enterprises are required to disclose or explain the outsourcing of labor services in their feedback. We are concerned that the main businesses of these enterprises that are required to give feedback on labor outsourcing are different, and the industries are distributed in the fields of construction, building materials and chemical industry, computer, logistics and transportation. In general, the outsourcing is mostly engineering construction work, and it is non-critical and auxiliary business. The primary concern of the CSRC is whether the intermediary agencies disclose the labor outsourcing truthfully, especially when the labor outsourcing costs account for a relatively high proportion or pose a significant risk to the issuer's business, the intermediary agencies are required to disclose the relevant information in detail according to the principle of "substance is more important than form", not only the specific situation of the labor outsourcing business and the reasons for outsourcing, the specific circumstances of the labor outsourcing unit should also be disclosed. 2. what is labor dispatch? According to the provisions of the the People's Republic of China Labor Contract Law (2012 Amendment) and the Interim Provisions on Labor Dispatch, labor dispatch refers to the labor dispatch unit with the qualification of labor dispatch business to conclude a labor contract with the laborer, and the labor dispatch unit then signs a labor dispatch agreement with the employing unit that needs the laborer. Finally, the labor dispatch unit sends the laborer to the employing unit to work. As a flexible way of employment, labor dispatch is usually used by enterprises to solve the problem of labor shortage, which can effectively save the labor cost of labor enterprises, especially in some labor-intensive enterprises. Its basic legal relationship is shown in the following figure: The Interim Provisions on Labor Dispatch stipulate that labor dispatch can only be implemented in temporary, auxiliary or alternative jobs: temporary jobs refer to jobs that last no more than 6 months; auxiliary jobs refer to non-main business jobs that provide services for main business jobs; alternative jobs refer to a certain period of time when the workers of the employing unit are unable to work due to off-duty study, vacation and other reasons, jobs that can be replaced by other workers. And the employing unit shall strictly control the number of dispatched workers, and the number of dispatched workers shall not exceed 10% of the total number of workers. In the practice of enterprise IPO, the employment method of labor dispatch is more common in labor-intensive enterprises. At the same time, in order to prevent the issuer from failing to sign labor dispatch contracts in accordance with the law and damage the legitimate rights and interests of dispatched employees during the reporting period, in the IPO declaration process, labor dispatch is often one of the issues that regulators focus on. 3. the difference between the two and audit points From the foregoing analysis, it follows that labor dispatch is a moderate separation of employment and use, and that labor outsourcing does not involve a separation of employment and use. That is, under the employment form of labor dispatch, the employing unit transfers the right to establish labor relations, but does not transfer the right to manage things and people. The labor of workers is completed under the supervision and management of the employing unit and is managed by the employing unit. In addition, in the actual operation process, we are concerned that the regulatory authorities in the filing process of the proposed IPO enterprises on the two audit points have the following differences: 1. The common audit concerns of regulatory agencies on labor outsourcing in the IPO declaration process are as follows:(1) whether the information disclosure is sufficient;(2) Independent judgment: comprehensively judge whether the enterprise has significant dependence on labor outsourcing suppliers and analyze the impact on the independence of the issuer;(3) Internal control: pay attention to the internal control and risk control measures related to the labor outsourcing link of the issuer;(4) The determination of labor outsourcing and labor dispatch: the situation of "false outsourcing, real dispatch" is more concerned. 2. The common audit concerns of regulatory agencies on labor dispatch issues during the IPO declaration process are as follows:(1) Whether the labor dispatch unit has an associated relationship with the issuer, and whether the related transactions are legal and compliant;(2) Whether all links of labor dispatch comply with The provisions of laws and regulations, whether there are circumstances that damage the legitimate rights and interests of workers;(3) Whether there are major violations or the risk of being punished. In summary, labor and employment compliance is an important part of corporate compliance operations and a basic requirement for companies to go public. Therefore, for the employment of enterprises, we should pay attention to the provisions of relevant laws and regulations, implement and arrange the corresponding production and operation plans in accordance with the relevant provisions of laws and regulations on labor dispatch and labor outsourcing, and not only ensure that the employment mode, number of people, posts, etc. meet the restrictions of relevant laws and regulations, but also examine the qualifications of the other party, it is not allowed to deliberately evade the obligations of the employer by means of labor dispatch or labor outsourcing. As for the intermediary agencies, they should judge the actual employment nature of the enterprise from the principle of "substance is more important than form", rather than simply judging according to the contract form signed by the enterprise. For the situation that the essence belongs to labor dispatch and there are violations, it should be regulated in time to avoid obstacles in the process of listing audit and affect the progress of listing.
2021-12-16
16
2021-12
On the morning of December 15, 2021, Zhang Hao, a lawyer from the Financial Investment Department of Zhongcheng Qingtai (Jinan) Law Firm, carried out the "Civil Code" for the Shandong Branch of China Three Gorges New Energy (Group) Co., Ltd. "Contract Signing and Risk Prevention" special lecture, related project companies participated in this lecture through a remote conference. As the main body of the strategic implementation of the new energy business of the Three Gorges Group, China Three Gorges New Energy (Group) Co., Ltd. carries the historical mission of developing new energy. Its legal compliance business has a strong professionalism and complexity, in order to help the company popularize The basic knowledge of the contract compilation of the Civil Code, prevent the risk of contract signing, and sort out the contract performance management process, lawyer Zhang Hao was invited to give this lecture. According to the existing litigation risks of Three Gorges New Energy Company, lawyer Zhang Hao took the case of Three Gorges New Energy Company as the starting point, and took the practical operation as the guide, and shared the legal knowledge of the change interpretation, contract design and risk prevention, contract signing and performance rules of the Civil Code. This lecture is rich in content, has a strong practical significance, and won the unanimous praise of the participants.
2021-12-16
16
2021-12
The Sixth Plenary Session of the 19th Central Committee of the Communist Party of China is a very important meeting held at the important historical moment of the centenary of the party and at the important historical juncture when the "two centenary" goals meet. The plenary session comprehensively summarized the party's major achievements and historical experience in a century of struggle, and has great practical significance and great practical significance for promoting the whole party to further unify its thinking, will, and action, and unite and lead the people of all ethnic groups across the country to win new great victories in socialism with Chinese characteristics in the new era. Far-reaching historical significance. In order to effectively do a good job in "learning the spirit of the sixth plenary session and practicing the original mission" and to educate and guide party members and lawyers to practice their internal skills, take strong responsibilities and work hard to promote development, on December 15, the party branch of Shandong zhongcheng Qingtai (Dezhou) law firm held a December theme party day activity in the party conference room on the 23rd floor. party branch secretary Wei jinhui and some party members attended the meeting, and party branch deputy secretary Li Jianhua presided over the meeting. In the first item of the meeting, Wei Jinhui, secretary of the party branch, led the study of the "Resolution of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China on the Major Achievements and Historical Experience of the Party's Centennial Struggle." The second item of the meeting was that the Party branch studied and determined that Comrade Li Dezhi was an active member of the Party. In the third item of the meeting, the party branch studied and determined the confirmation of comrade Zhu min's probationary party member. Subsequently, the party branch will assign points to each party member according to the implementation plan of quantitative points for party members, and summarize the annual points of each party member. Li Jianhua, deputy secretary of the "rule of law for private practical" publicity activities to carry out a briefing. Zhongcheng Qingtai actively organized lawyers to enter communities, schools, and enterprises to carry out legal services and legal aid work, volunteered for more than a thousand times, subsidized a number of outstanding college students, and sent warmth to disabled children, which has won wide praise from all walks of life. Secretary Wei Jinhui finally emphasized that all lawyers must thoroughly study, publicize and implement the spirit of the Sixth Plenary Session of the 19th Central Committee of the Party, closely connect with the actual work, fully complete the annual tasks, and learn and implement the spirit of the Sixth Plenary Session of the 19th Central Committee of the Party. Effectively transform the spiritual achievements of the Sixth Plenary Session into serving the overall situation, serving the people, and doing every legal affairs well with heart, affection, welcome the 20th National Congress of the Communist Party of China with outstanding achievements, and use practical actions to provide assistance to promote the construction of the rule of law.
2021-12-16
16
2021-12
Recently, the Shandong Provincial National Intellectual Property Protection Center decided to award 50 units including Zhongcheng Qingtai Law Firm as the first batch of fast rights protection stations to provide fast rights protection services for the main body of the Shandong Provincial National Intellectual Property Protection Center. Zhongcheng Qingtai Law Firm has a large number of high-level expert teams in the field of intellectual property legal services such as patents, trademarks, copyrights, etc., providing satisfactory protection solutions and performance for the intellectual creativity and technological innovation of a wide range of client groups. Previously, many lawyers from Zhongcheng Qingtai have been selected into the talent expert pool of the provincial protection center. This time, Zhongcheng Qingtai has been approved as the first batch of rapid rights protection stations. It will continue to help relevant filing subjects realize all-round protection of technical barriers and brand advantages through its own professional and dedicated services, and help the rapid rights protection of intellectual property rights to achieve a new level.
2021-12-16
15
2021-12
[brief case]] In 2012, a Tianjin Beverage Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as "Tianjin Beverage Company") signed a one-year house lease contract with a scientific research institute in Chengde (now "Chengde Academy of Sciences"), agreeing that the company would lease the warehouse of the institute to store products and equipment. In December of the same year, a beverage company in Tianjin insured all risks to the Beijing branch of an insurance company. On April 20, 2013, an electrician of a scientific research institute in Chengde illegally operated, causing a fire in the warehouse, and the items stored in the warehouse of a beverage company in Tianjin were burned. Later, the Higher People's Court of Hebei Province determined in a separate civil judgment that the electrician's behavior was an act of duty, and the institute was mainly liable for compensation for the accident. After the accident, a beverage company in Tianjin applied for a claim to the Beijing branch of an insurance company for the loss of the accident. Beijing Branch of an insurance company paid insurance compensation of 2.5 million yuan and more than 1.92 million yuan to a beverage company in Tianjin on June 9, 2013 and November 11, 2014 respectively according to the insurance contract. On November 9, 2016, the Beijing branch of an insurance company filed a subrogation lawsuit with the People's Court of Shuangqiao District, Chengde City, Hebei Province. The first-instance judgment found that the first insurance compensation of 2.5 million yuan had passed the statute of limitations for subrogation. The claim for the insurance money was not supported. Later, the company appealed to the Intermediate People's Court of Chengde City, Hebei Province, and the original judgment was upheld in the second instance. In 2018, the company applied for a retrial, and the Hebei Provincial higher people's Court made a retrial judgment on November 29, 2018, finding that the first insurance compensation of 2.5 million yuan did not exceed the statute of limitations, and decided to revoke the 1. judgment of second instance. A scientific research institute in Chengde should pay compensation for fire losses to the Beijing branch of an insurance company within the scope of full insurance compensation in accordance with the proportion of fire accident liability. focus of controversy] Whether the insurance compensation claimed by the insurance company exceeds the statute of limitations. The court of first instance held that] According to the first paragraph of Article 60 of the the People's Republic of China Insurance Law, the insurance company must meet the following conditions to exercise the right of recovery: first, the insurance company has compensated the insured for the insurance money; second, the loss of the subject matter of the insurance is caused by the damage of a third party. In this case, the insurance contract relationship between a Tianjin beverage co., ltd. and the plaintiff is legal and valid. the plaintiff has paid compensation for the actual losses of a Tianjin company caused by the accident according to the insurance contract between the two parties. therefore, the plaintiff has the right to claim subrogation from a certain academy of sciences in Chengde city for 60% of the insurance premium payable. According to the provisions of Article 16, paragraph 2, of the (II) of the Supreme People's Court on the Interpretation of Several Issues Concerning the Application of the the People's Republic of China Insurance Law, the limitation period for the insurer's right of subrogation shall be calculated from the date on which it obtains the right of subrogation. According to the first paragraph of Article 60 of the Insurance Law, the insurer shall, from the date of compensation to the insured, exercise the right of the insured to claim compensation from a third party within the scope of the amount of compensation. Therefore, the date on which the insurer obtains the subrogation claim is the date on which its insurance is paid. In this case, the plaintiff paid insurance compensation of RMB 2500000 yuan and RMB 1920296.79 yuan to a company in Tianjin on June 9, 2013 and November 11, 2014 respectively. On June 9, 2013, the plaintiff's first insurance compensation of RMB 2500000 yuan obtained the right of subrogation against an academy of sciences in Chengde City. On November 11, 2014, the plaintiff's second insurance compensation of RMB 1920296.79 yuan obtained the right of subrogation against an academy of sciences in Chengde City. This case is a dispute over damages between the plaintiff, a Beijing branch of an insurance company, acting on behalf of a company in Tianjin, and the defendant. It is a lawsuit based on the debt of infringement. The limitation period of action should be two years. The limitation period for the plaintiff's first insurance compensation is from June 10, 2013 to June 9, 2015. According to Article 140 of the General Principles of Civil Law, the limitation of action is interrupted by the initiation of a lawsuit, the request of one of the parties or the consent to perform the obligation. The limitation period is recalculated from the time of the interruption. Article 10 of the Provisions of the Supreme People's Court on Several Issues Concerning the Application of the Limitation of Action System in the Trial of Civil Cases stipulates that under any of the following circumstances, it shall be deemed as "a request by one of the parties" stipulated in Article 140 of the General Principles of Civil Law, which shall have the effect of interruption of the limitation of action: (2) One of the parties claims its rights by sending letters or data messages, and the letters or data messages arrive or data messages should arrive or reach the other parties. In this case, a law firm in Beijing sent a lawyer's letter EMS on claiming compensation to a scientific research institute in Chengde City on June 9, 2015. The lawyer's letter did not attach the plaintiff's authorization document. In combination with a law firm in Beijing as the agent of the insurer and the insured in the warehouse fire series case, it could not be determined that it claimed the right to a certain person in Chengde City based on the authorization act. In addition, the EMS did not arrive at the defendant on June 9, 2015, and could not interrupt the statute of limitations for the first insurance compensation. The statute of limitations for the first insurance compensation of 2500000 yuan has passed for the past two years. In this case, the limitation period of action for the second insurance compensation of 1920296.79 yuan was calculated from November 11, 2014 to November 9, 2016. The plaintiff filed a lawsuit with Chengde intermediate people's court, and the limitation period of action for the second insurance compensation of 1920296.79 yuan was not expired. According to the provisions of Article 60 of the Insurance Law, the scope of the insurer's exercise of the right of subrogation is limited to the insurance compensation paid, and the loss of interest after the insurer pays the compensation shall not be claimed to a third party. In accordance with Article 60 of the the People's Republic of China Insurance Law, Article 16 of the Interpretation (II) of the Supreme People's Court on Several Issues Concerning the Application of the the People's Republic of China Insurance Law, Article 140 of the General Principles of the Civil Law, Item (II) of Article 10 of the Provisions of the Supreme People's Court on Several Issues Concerning the Application of the Limitation of Action System in the Trial of Civil Cases, and Article 144 of the the People's Republic of China Civil Procedure Law, the judgment: the 1. defendant, a scientific academy of sciences in Chengde city, shall compensate the plaintiff for 1152178.07 yuan (1920296.79 X60%) of the Beijing branch of an insurance company within 15 days after the judgment comes into effect. The 2. defendant, a trading co., ltd. in Chengde city, shall not be liable for compensation; The 3. rejected other claims of the plaintiff's Beijing branch of an insurance company. The court of second instance held that] After the insurance accident occurred, the Beijing branch of an insurance company paid insurance compensation of RMB 2500000.00 yuan and RMB 1920296.79 yuan to a company in Tianjin on June 9, 2013 and November 11, 2014 respectively according to the insurance compensation request of the insured company in Tianjin and the relevant accident materials provided, indicating that the Beijing branch of an insurance company should know the infringer and infringement when paying the first insurance compensation, and an insurance company Beijing branch did not provide evidence to prove that the two insurance compensation payment methods are agreed by both parties or the legal provisions of the installment payment method, so the two insurance compensation statute of limitations should be calculated separately. The limitation period for the first insurance compensation is from June 10, 2013 to June 9, 2015. Although a law firm in Beijing sent a lawyer's letter claiming compensation to a scientific research institute in Chengde City through EMS on June 9, 2015, the lawyer's letter did not attach the authorization document of a Beijing branch of an insurance company, and it cannot be determined that it claimed rights from a certain company in Chengde City based on the authorization act, and the lawyer's letter did not arrive on June 9, 2015, there is no interruption of the statute of limitations for the first insurance compensation. The judgment of the original court that after the Beijing branch of an insurance company paid the first insurance compensation of 2500000 yuan to a Tianjin company, it claimed this right to a scientific research institute in Chengde city after two years of limitation of action was found to be not improper. The scope of the Beijing branch of an insurance company exercising the right of subrogation as an insurer is limited to the insurance compensation paid in accordance with the provisions of Article 60 of the Insurance Law. The judgment of the court of first instance against the claim of interest of an insurance company Beijing Branch was not supported, and there was nothing improper. In summary, the appellant's appeal request from the Beijing branch of an insurance company cannot be established and should be rejected. The first-instance judgment has clear facts and the applicable law is correct and should be maintained. The retrial court held that] On the question of whether an insurance company's Beijing branch claimed to a Chengde academy of sciences whether the 2500000 yuan insurance compensation exceeded the statute of limitations. The Supreme People's Court on the application
2021-12-15
15
2021-12
A private equity fund (Private Fund) is an investment fund that raises funds from specific investors in a non-public manner and invests in a specific target. Private equity funds are recruited by means other than mass communication, and the promoters pool the funds of non-public diversified subjects to set up investment funds to invest in securities. With the improvement of China's financial and economic system, private equity funds have become a financial investment method recognized and supported by the state. At the same time, in order to regulate private equity fund activities, protect the legitimate rights and interests of investors and related parties, and promote the healthy development of the private equity investment fund industry, the China Securities Regulatory Commission has successively formulated and implemented the Interim Measures for the Supervision and Administration of Private Equity Investment Funds, and Securities and Futures Laws and regulations such as the Interim Provisions on the Operation and Management of Private Equity Asset Management Business of Operating Institutions, and the Provisions on Strengthening the Supervision of Private Equity Investment Funds. From the definition of private equity funds can be seen, fund raising, investment, the pursuit of return is the core of the main line of private equity funds. Private equity funds can easily trigger legal risks in the process of product design, management and operation, and even exit, especially the criminal legal risks of illegal fund-raising. According to the statistics of judicial practice, illegal fund-raising crimes have become the top ten high-incidence crimes among the 483 crimes in the Criminal Law, and more than 70% of the crimes triggered by private equity activities are illegal fund-raising crimes. Therefore, practitioners and related personnel in the field of private equity funds should pay close attention to the criminal legal risks of illegal fund-raising, and prevent violations of criminal law due to improper operation and triggering criminal legal risks. Illegal fund-raising is an act of absorbing funds from the public (including units and individuals) in violation of national financial management laws. In view of the complexity of illegal fund-raising criminal activities, in order to facilitate practical grasp, the "Judicial Interpretation of Illegal Fund-raising" specifically refines the elements of illegal fund-raising behavior, and clarifies that the establishment of illegal fund-raising needs to be illegal, open, inducement, and social. Four characteristics:(1) Absorbing funds without the approval of relevant departments in accordance with the law or borrowing the form of legal operations;(2) Publicize to the public through the media, promotion conferences, leaflets, mobile phone text messages, etc.;(3) Promise to repay the principal and interest or pay returns in currency, in kind, equity, etc. within a certain period of time;(4) To absorb funds from the public, that is, non-specific objects of society. 1. to avoid violating the national financial management laws and regulations, to prevent the violation of "illegal" characteristics With regard to private equity funds, China adopts the registration and filing system of the China Securities Investment Fund Industry Association, that is, the fund manager needs to register with the fund industry association; after the private equity fund is raised, the private equity fund manager shall, in accordance with the provisions of the fund industry association, handle the fund filing procedures. The above registration and filing are mandatory provisions, and fund managers must strictly abide by them. Violation of the above provisions is "violation of national financial management laws and regulations" and "without the approval of relevant national competent departments". Article 1 of the "Opinions on Several Issues Concerning the Handling of Criminal Cases of Illegal Fund-raising" issued by the Supreme People's Court, the Supreme People's Procuratorate, and the Ministry of Public Security in January 2019 stipulates the basis for determining the "illegality" of illegal fund-raising. The people's courts, people's procuratorates, and public security organs shall determine the "illegality" of illegal fund-raising based on national financial management laws and regulations. If the national financial management laws and regulations are only stipulated in principle, they can be determined in accordance with the spirit of the law and with reference to the departmental rules formulated by the people's Bank of China, the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission, the China Securities Regulatory Commission and other administrative departments in accordance with the national financial management laws and regulations or the provisions of the state's relevant financial management regulations, measures, implementation rules and other normative documents. Accordingly, the "Interim Measures for the Supervision and Administration of Private Investment Funds" and other provisions issued by the China Securities Regulatory Commission can be used as a legal basis for judging whether private equity behavior has the characteristics of "illegality. Because the "Interim Measures" have made relevant provisions on the qualifications of fund-raising entities, fund-raising methods, fund-raising objects, and sources of fund-raising, violating these provisions is also a violation of "violation of national financial management laws and regulations". Of course, it is not that private equity funds have full legitimacy as long as they have gone through the registration and filing procedures, but failure to carry out legal registration and filing directly violates the constitutive element of "without the approval of the relevant national authorities. 2. standardize the way funds are raised to prevent violations of the "openness" feature. Private placement, as the name implies, is limited to "non-public" in the way of raising funds ". Article 6 of the "Several Provisions on Strengthening the Supervision of Private Equity Investment Funds" of the China Securities Regulatory Commission clearly stipulates that "private equity fund managers, private equity fund sales agencies and their employees shall not directly or indirectly have the following behaviors in the process of private equity fund raising: through newspapers, radio, Television, Internet and other public communication media, lectures, reports, analysis meetings, etc, notices, leaflets, text messages, instant messaging tools, blogs and e-mails and other carriers to promote and promote to unspecified targets." Therefore, any form of public communication, direct, indirect or otherwise, is prohibited by regulation. Private equity fund managers, private equity fund sales institutions and their practitioners should strictly abide by this provision, otherwise they will violate the "openness" feature. 3. improve the examination measures of qualified investors, penetrate the examination of qualified investors, and prevent the violation of "social" characteristics. According to the Measures for the Administration of the Suitability of Securities and Futures Investors, the Measures for the Administration of Private Investment Fund Raising Behavior, and the Instructions for the Filing of Private Investment Funds, private equity fund managers, private equity fund sales agencies and their practitioners should conduct the following two aspects Review. First, the verification of investors' risk identification ability and affordability. The specific verification standards are clearly stipulated in the "Measures for the Supervision and Administration of Private Investment Funds": (1) The amount invested in a single private equity fund shall not be less than 1 million yuan;(2) The net assets of unit investors shall not be less than 10 million yuan;(3) Personal financial assets shall not be less than 3 million yuan or the average annual personal income in the last three years shall not be less than 500000 yuan." Second, the number of qualified investors is limited: the number of investors in a single private equity fund shall not exceed the number of restrictions stipulated in the Company Law, the Partnership Law, and the Securities Investment Fund Law. The maximum number of legal fundraisers for partnership and corporate private equity funds is 50. In terms of review measures, it is possible to verify whether the investor (legal person) meets the criteria for qualified investors by reviewing the year-end net assets, audited financial statements, financial asset supporting documents, personal annual income and other evidentiary materials. Where a private equity fund manager sells private equity funds on its own, it shall adopt questionnaires and other methods to evaluate the investor's risk identification ability and risk-bearing ability, and the investor shall make a written commitment to meet the conditions of qualified investors. Where a private equity fund manager entrusts a sales agency to sell a private equity fund, the private equity fund sales agency shall take the measures such as the evaluation and confirmation provided for in the preceding paragraph. The content and format guidelines of the questionnaire and risk disclosure letter of investors' risk identification ability and bearing ability are formulated by the fund industry association according to the characteristics of different types of private equity funds. In response to the phenomenon of "holding on behalf" to circumvent the restrictions on the number of private equity funds and investment limits, the "Instructions for the Filing of Private Equity Funds" stipulates: "For private equity funds invested in the form of partnerships and other illegal entities, the raising institution shall penetrate to verify whether the final investor is a qualified investor and calculate the number of investors in combination." In response to the issue of private equity fund share transfer, the "Private Investment Fund Filing Instructions" stipulates: "The fundraising institution shall ensure that the investor is aware of the private equity fund transfer conditions, and the investor shall promise in writing to purchase the private equity fund for himself, and complete the private equity fund risk disclosure After that, the fundraising institution shall require investors to provide necessary asset certification documents or income certification." At the specific operational level of private equity funds, the qualification verification of qualified investors is an important aspect to ensure the legitimacy of the object of raising funds, and also an important guarantee to ensure that private equity funds raise funds from "specific objects. 4. standardize propaganda behavior, grasp the distribution principle of benefit sharing, risk sharing, risk and income matching, and prevent the violation of "inducement" characteristics. Article 1 of the Supreme People's Court's Interpretation on Several Issues Concerning the Specific Application of Laws in the Trial of Criminal Cases of Illegal Fund-raising stipulates: "Violation of national financial management laws and regulations, the act of absorbing funds from the public (including units and individuals) meets the following four conditions. Unless otherwise provided in the Criminal Law, it shall be deemed as" illegal absorption of public deposits or absorption of public deposits in disguised form "as stipulated in Article 176 of the Criminal Law: promise to repay principal and interest or pay returns in money, in kind, equity, etc. within a certain period of time." This is the provision for the "inducement" feature, which is commonly referred to as "capital preservation". And private equity fund is a kind of investment behavior, income and risk go hand in hand. Private equity fund managers and private equity fund sales institutions shall not promise investors that the principal of the investment shall not be lost or that the minimum return shall be promised, the expected return shall not be promised, and the performance comparison shall not be publicized. The Interim Provisions on the operation and management of private equity asset management business of securities and futures operating institutions issued by China Securities Regulatory Commission clearly states that "securities and futures operating institutions and relevant sales institutions shall not sell asset management plans in violation of regulations, and shall not have improper publicity, mislead and cheat investors, or promise to investors in any way without loss of principal or minimum income, Including but not limited to the following situations: there are expressions in asset management contracts and sales materials that contain the connotation of capital preservation, such as zero risk, guaranteed income, and worry-free principal; The name of the asset management plan contains the word "capital preservation"; sign repurchase agreements or commitment letters and other documents with investors in private, and directly or indirectly promise capital preservation and income protection; promise capital preservation and income protection to investors orally or through various methods such as SMS and WeChat; Promote the expected rate of return of the asset management plan to investors; Exaggerate or one-sided promote products, exaggerated or one-sided publicity of the past performance of the asset management plan manager and the products under his management, investment managers, etc., did not fully disclose the product risks, and investors did not sign risk disclosure letters and asset management contracts when subscribing to the asset management plan. For structured funds that are more likely to violate the characteristics of "inducement" in judicial practice, the "Interim Regulations" specifically clarify: "The establishment of structured asset management plans by securities and futures operating institutions shall not violate benefit sharing, risk sharing, and matching of risks and returns. The following situations shall not exist: (1) Directly or indirectly provide capital protection and income arrangements to subscribers of priority shares, including but not limited to the provision of priority share income, early termination penalty interest, inferior or third-party institutions to make up the difference of priority income, provision of risk margin to make up the priority income, etc. agreed in the contract of structured asset management plan; (II) fail to conduct sufficient and appropriate due diligence on the identity and risk bearing capacity of inferior share subscribers of structured asset management plan; the (III) fails to fully disclose and disclose the structured design and corresponding risk situation, income distribution, wind control measures and other information in the asset management contract; The leverage ratio of (IV) stock and hybrid structured asset management plans exceeds 1 times, the leverage ratio of fixed income structured asset management plans exceeds 3 times, and the leverage ratio of other types of structured asset management plans exceeds 2 times. It is (V) to check the investment target of structured asset management plans through penetration, the structured asset management plan nests and invests in the inferior share of other structured financial products; the name of the (VI) structured asset management plan does not contain the words" structured "or" graded "; the total assets of the (VII) structured asset management plan account for more than 140 per cent of net assets, and the total assets of the unstructured collective asset management plan (I. e." one-to-many ") account for more than 200 per cent of net assets." On the issue of credit enhancement measures such as guarantees provided by third parties. First of all, the credit enhancement measures can not be simply identified as "capital preservation and income protection"; second, it is not prohibited to take relevant credit enhancement measures in the asset management plan from the level of laws and regulations; third, it should be legal, true and effective in the implementation of third-party credit enhancement measures, so as to prevent the occurrence of credit enhancement measures as a means of "capital preservation and income protection" in disguise. With respect to premium repurchase and gambling agreements, attention should be paid to the design of the trigger clause in the Equity or Fund Share Repurchase Agreement to prevent the occurrence of an agreement on the contingency of the achievement of the condition as inevitable. With regard to the dividend mechanism, the issue of the source of dividend funds should be strictly grasped. Dividend funds should be derived from the investment income of the fund, not the fund itself, otherwise it may be found to be in line with the characteristics of "inducement" in judicial practice.
2021-12-15

Zhongcheng Qingtai Jinan Region
Address: Floor 55-57, Jinan China Resources Center, 11111 Jingshi Road, Lixia District, Jinan City, Shandong Province